Smart ligands
Smart ligands are affinity ligands selected with pre-defined equilibrium (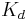 ), kinetic (
), kinetic (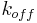 ,
, 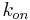 ) and thermodynamic (ΔH, ΔS) parameters of biomolecular interaction.
) and thermodynamic (ΔH, ΔS) parameters of biomolecular interaction.
Ligands with desired parameters can be selected from large combinatorial libraries of biopolymers using instrumental separation techniques with well-described kinetic behaviour, such as Kinetic capillary electrophoresis (KCE), Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR), Microscale Thermophoresis (MST)[1][2] and etc. Known examples of smart ligands include DNA smart aptamers; however, RNA and peptide smart aptamers can also be developed.
Smart ligands can find a set of unique applications in biomedical research, drug discovery and proteomic studies. For example, a panel of DNA smart aptamers has been recently used to develop affinity analysis of proteins with ultra-wide dynamic range of measured concentrations.
References
- ^ Baaske P, Wienken CJ, Reineck P, Duhr S, Braun D (Feb 2010). "Optical Thermophoresis quantifies Buffer dependence of Aptamer Binding". Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 49 (12): 1–5. doi:10.1002/anie.200903998. PMID 20186894. Lay summary – Phsyorg.com.
- ^ Wienken CJ et al. (Oct 2010). "Protein-binding assays in biological liquids using microscale thermophoresis". Nature Communications 1 (7): 100. Bibcode 2010NatCo...1E.100W. doi:10.1038/ncomms1093. http://www.nature.com/ncomms/journal/v1/n7/full/ncomms1093.html.
- Drabovich AP, Berezovski MV, Musheev MU, Krylov SN (January 2009). "Selection of smart small-molecule ligands: the proof of principle". Anal. Chem. 81 (1): 490–4. doi:10.1021/ac8023813. PMID 19055427.
- Drabovich A, Berezovski M, Krylov SN (August 2005). "Selection of smart aptamers by equilibrium capillary electrophoresis of equilibrium mixtures (ECEEM)". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 127 (32): 11224–5. doi:10.1021/ja0530016. PMID 16089434.
- Drabovich AP, Berezovski M, Okhonin V, Krylov SN (May 2006). "Selection of smart aptamers by methods of kinetic capillary electrophoresis". Anal. Chem. 78 (9): 3171–8. doi:10.1021/ac060144h. PMID 16643010.
- Drabovich AP, Okhonin V, Berezovski M, Krylov SN (June 2007). "Smart aptamers facilitate multi-probe affinity analysis of proteins with ultra-wide dynamic range of measured concentrations". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 129 (23): 7260–1. doi:10.1021/ja072269p. PMID 17503828.
- Krylov SN (January 2007). "Kinetic CE: foundation for homogeneous kinetic affinity methods". Electrophoresis 28 (1–2): 69–88. doi:10.1002/elps.200600577. PMID 17245689.